/* Style Definitions */
table.MsoNormalTable
{mso-style-name:”Table Normal”;
mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0;
mso-tstyle-colband-size:0;
mso-style-noshow:yes;
mso-style-priority:99;
mso-style-qformat:yes;
mso-style-parent:””;
mso-padding-alt:0cm 5.4pt 0cm 5.4pt;
mso-para-margin-top:0cm;
mso-para-margin-right:0cm;
mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt;
mso-para-margin-left:0cm;
line-height:115%;
mso-pagination:widow-orphan;
font-size:11.0pt;
font-family:”Calibri”,”sans-serif”;
mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri;
mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin;
mso-fareast-font-family:”Times New Roman”;
mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-fareast;
mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri;
mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
Thank you Dr Verner Wheelock for the extensive critique of the reports . The Cochrane reports analysis was heroic and well structured. We had a huge debate about them at the time on THINCS (www.thincs.org).
For my part I shy away from statistical analysis which doesn’t include ‘All Cause Mortality’ figures. The reason being that failure to look at all the non-cardio deaths and drop-outs from trials cleans and amplifies the apparent benefits of Statins. This means we can never know the Numbers Needed to Harm NNH side of the medication.
My first ever review paper (G Wainwright et al., 2009) looking at the clinical impact of cholesterol lowering in all non-cardiovascular organs, was seminal in that it pointed up a fundamental flaw in the whole statin concept i.e. Cholesterol is vital and inhibiting its production is destined to create a wide and varied set of Adverse Events in statin users in the longer term. That is why ‘all cause mortality’ data is not made available (caveat emptor).
In our second review paper(Seneff et al., 2011) we became aware of the fact that LDL/HDL ratios were associated with LDL consumption by organs and not production by the liver. The whole LDL argument had been inverted. If LDL is damaged by glycation, LDL goes up and HDL falls. The liver’s glycated-LDL is unused and the corresponding HDL return to the liver does not happen.
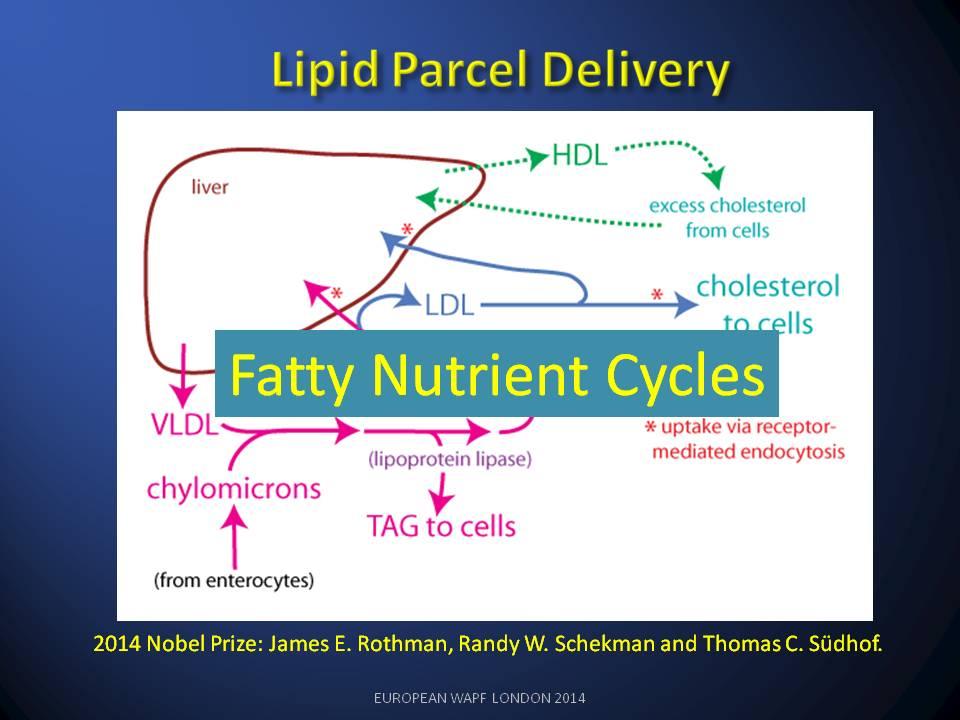
How such a fundamental part of the lipid nutrition cycle could be missed is hard to understand. Obsession with statins and statin finance has done immense harm to cardio-medicine and I believe we are seeing the start of a major NICE scandal as the BMA object to the guidance.



